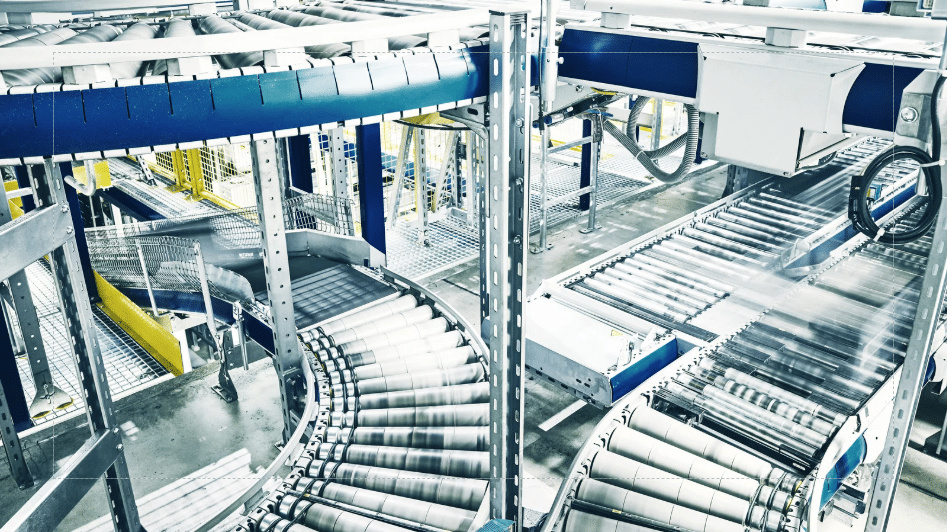
In industries where the efficient movement of goods is critical, conveyors play an essential role. Among the various types, powered roller conveyors and motorized drive roller (MDR) conveyors are popular choices. Both serve the purpose of transporting goods, but their functionality, design, and applications vary significantly.
When it comes to selecting the right conveyor system, understanding the unique features and capabilities of each type is essential. Powered roller conveyors and MDR conveyors are engineered for specific operational needs, making them suitable for different industries. While they might seem similar at first glance, their core differences lie in their driving mechanisms, energy efficiency, and application scope.
What are Powered Roller Conveyors?
Powered roller conveyors are mechanical systems used to transport goods and materials along a production line or warehouse floor. Unlike traditional conveyors, which require manual effort or gravity to move items, powered roller conveyors are equipped with motorized rollers that provide automated movement. These systems can handle various loads, from lightweight packages to heavy industrial items, making them versatile for industries such as manufacturing and distribution. The powered rollers are typically controlled by motors, sensors, and programmable systems, allowing for efficient and precise handling of goods across different stages of the workflow.
One of the significant advantages of powered roller conveyors is their ability to optimize productivity while reducing manual labor. They can be configured to accommodate straight, curved, or inclined paths, making them suitable for complex layouts. Additionally, these conveyors often include features such as variable speed settings, zone control, and automatic stopping mechanisms to enhance safety and energy efficiency. Their modular design allows for easy expansion or reconfiguration as operational needs evolve, making powered roller conveyors an essential component in modern logistics and industrial applications.
The driving mechanism can include:
- Belt-driven rollers: A continuous belt drives the rollers, creating a uniform movement.
- Chain-driven rollers: Chains transfer power to the rollers, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Line-shaft-driven rollers: A rotating shaft connected to spools drives the rollers.
Key Features of Powered Roller Conveyors
- High Load Capacity: Ideal for transporting heavy loads, such as pallets, cartons, or large boxes.
- Continuous Movement: Suitable for long-distance operations, ensuring uninterrupted flow.
- Durability: Built for rugged use in industrial environments.
- Centralized Motor System: A single motor or few motors drive the entire conveyor line.
What Are MDR (Motorized Drive Roller) Conveyors?
Motorized Drive Roller (MDR) conveyors are a type of conveyor system that utilizes motorized rollers to transport materials along a defined path. Unlike traditional conveyor systems that rely on external motors and chains or belts, MDR conveyors integrate small motors directly within the rollers themselves. This design not only eliminates the need for additional mechanical components but also offers precise control over the movement of goods. Each motorized roller can operate independently or in coordination with others, enabling zoned control for better efficiency. MDR conveyors are highly adaptable and are commonly used in industries like e-commerce, manufacturing, and logistics for handling lightweight to medium-weight items.
The advantages of MDR conveyors extend beyond their compact design. They are energy-efficient, as the motors activate only when needed, reducing power consumption compared to conventional systems that run continuously. Additionally, their modular design simplifies maintenance and scalability, allowing businesses to expand or reconfigure their systems as needed. With their ability to minimize noise, provide gentle handling of products, and enhance operational flexibility, MDR conveyors have become a preferred choice for modern material handling solutions.
Key Features of MDR Conveyors
- Individual Roller Motors: Each roller contains its own motor, enabling independent operation.
- Energy Efficiency: Operates only when needed, reducing energy consumption.
- Modularity: Sections can be added or removed with ease, offering scalability.
- Low Noise: Quieter compared to traditional powered roller conveyors.
- Safety: Lower operating forces reduce the risk of injuries.
Differences Between Powered Roller Conveyors and MDR
While both conveyor systems are essential for transporting goods, they have distinct characteristics and applications. Below is a detailed comparison highlighting their differences:
- Driving Mechanism
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Utilizes a centralized motor system that powers multiple rollers through interconnected components like belts, chains, or shafts. This design operates the rollers as a single unit. - MDR Conveyor:
Employs individual motors embedded within each roller, allowing localized and independent control of specific rollers or conveyor sections.
- Energy Efficiency
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Operates continuously, even when there are no goods to transport, resulting in higher energy consumption. It is less energy-efficient in low-load scenarios. - MDR Conveyor:
Activates only the rollers required for moving goods. This on-demand operation significantly reduces energy usage, making it more efficient for varying workloads.
- Load Capacity
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Built to handle heavy loads, these conveyors are robust and suited for industries like manufacturing and warehousing where large, bulky goods are common. - MDR Conveyor:
Designed for lighter loads, such as small packages, making them ideal for applications like e-commerce, parcel handling, and light industrial tasks.
- Noise Levels
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Tends to produce higher noise levels due to the centralized motor, mechanical linkages, and continuous operation of all rollers. - MDR Conveyor:
Operates quietly because of low-energy motors in individual rollers, providing a quieter work environment, especially in areas with high human activity.
- Control and Flexibility
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Offers limited control over individual rollers, as the system functions as a whole. It is less adaptable for tasks requiring sorting or accumulation. - MDR Conveyor:
Provides precise control over specific rollers or zones, enabling advanced features like accumulation, sorting, and selective movement of goods for greater flexibility.
- Maintenance
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Requires regular maintenance of its mechanical components, including belts, chains, and centralized motor systems. Downtime can affect the entire conveyor line. - MDR Conveyor:
Easier to maintain since each motorized roller operates independently. Repairs or replacements can often be done without disrupting the whole system.
- Applications
- Powered Roller Conveyor:
Preferred for heavy-duty tasks in environments such as manufacturing plants, large warehouses, and distribution centers where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. - MDR Conveyor:
Ideal for precision-based operations in retail, e-commerce, and light industrial settings, where speed, efficiency, and quiet operation are essential.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Powered Roller Conveyors | Powered Roller Conveyors |
| – Handles heavier loads. | – Higher energy consumption. |
| – Cost-effective for large-scale, continuous operations. | – Louder operation. |
| – Robust and durable for industrial environments. | – Limited modularity and control. |
| MDR Conveyors | MDR Conveyors |
| – Energy-efficient and cost-saving over time. | – Higher initial investment. |
| – Quiet and safe operation. | – Limited load capacity compared to powered roller conveyors. |
| – Flexible and scalable for growing businesses. |
How to Choose the Right Conveyor System
Choosing between powered roller conveyors and MDR conveyors depends on your specific business needs. Consider the following factors:
- Load Requirements
- Heavy loads: Powered roller conveyors are ideal for handling substantial weight.
- Light to medium loads: MDR conveyors are better suited for smaller, less heavy items.
- Energy Efficiency
- If reducing energy consumption is essential, MDR conveyors are designed for energy-efficient operation.
- Space and Scalability
- MDR conveyors are modular and highly adaptable, making them perfect for businesses planning flexible layouts or future expansions.
- Budget
- Powered roller conveyors are cost-effective initially.
- MDR conveyors may have a higher upfront cost but offer savings in energy consumption and maintenance over time.
- Noise Sensitivity
- For environments requiring quiet operation, such as retail stores or offices, MDR systems are the better choice.
By assessing these factors, you can choose a conveyor system that aligns with your operational needs and long-term goals.
Conclusion
Powered roller conveyors are great for handling heavy loads because they are strong and durable. On the other hand, MDR (Motorized Drive Roller) conveyors are known for saving energy, being flexible, and offering safety. Both types help improve productivity, but the best choice depends on what your business needs.
Choosing the right conveyor system can make your operations smoother, cut costs, and boost efficiency. By understanding your specific needs and comparing them with what these conveyor systems offer, you can make a smart decision that improves your work process and saves money.
If you’re looking for reliable and innovative packaging solutions, check out AFA Systems Inc.. We specialize in advanced cartoning, case packing, palletizing, case erectors, and robotic systems to meet diverse industry needs. Explore our cutting-edge technologies and transform your packaging process today!